Safety
Safe Project Design
Choosing parts that will not harm humans & animals
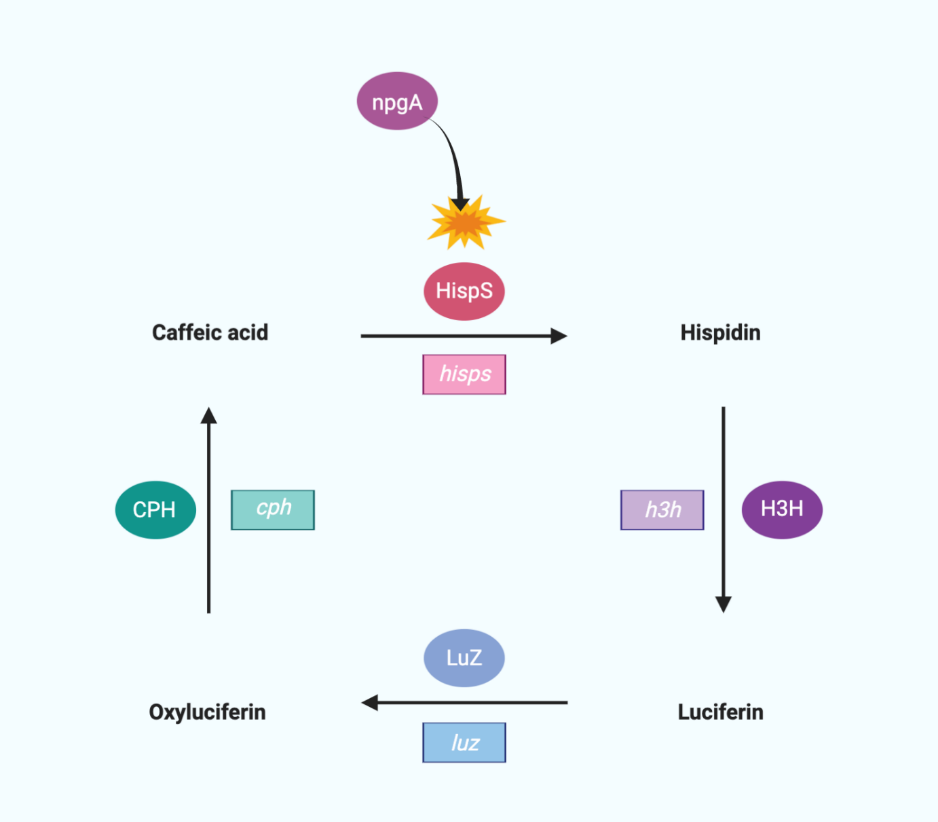
We chose a bioluminescent circuit which originates form fungi Neonothopanus nambi.
The expression of genes from the fungal bioluminescent pathway is not toxic to eukaryotic cells unlike bacterial pathway which has limited application in eukaryotes.
Choosing safer introducing method
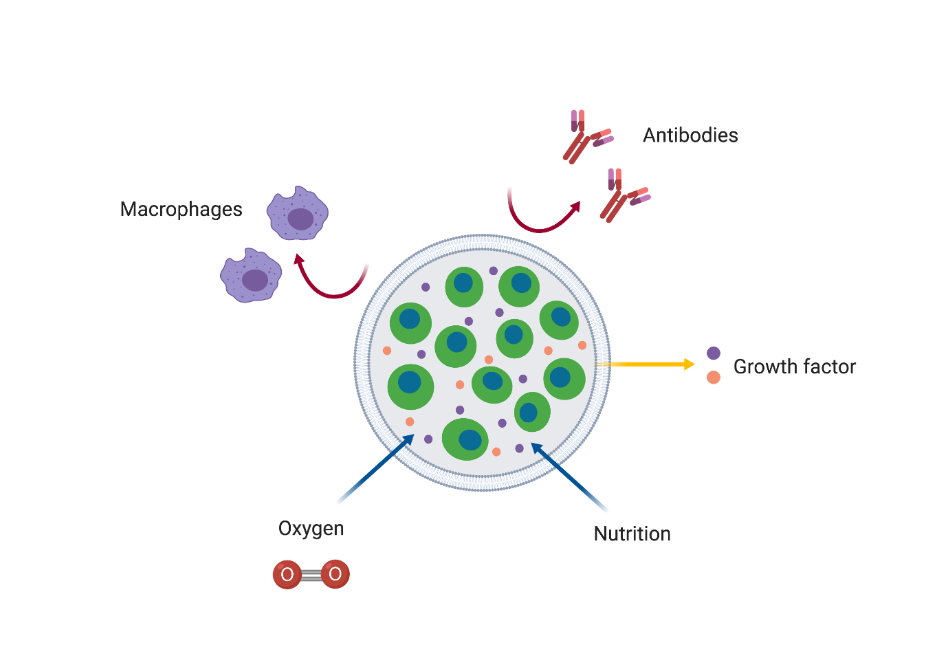
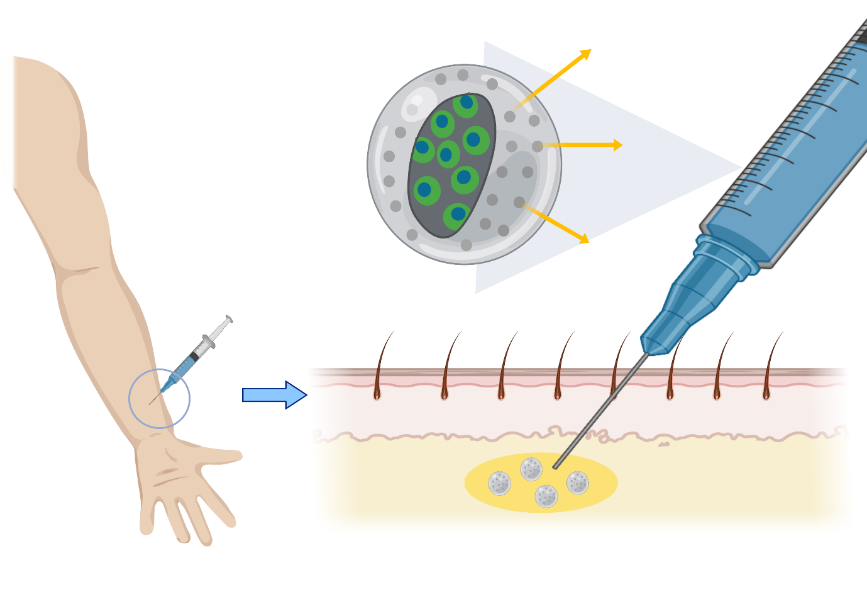
After introducing the gene circuit into the cells, the encapsulation method was chosen as the method for inserting the cells onto the skin surface.
Encapsulation method….
1. is safe because it can selectively transmit material compared to other methods (stem cells, nano-needle)
In this application, therapeutic cells are encapsulated in membranes that protect the cells against antibodies and cytotoxic cells of the host immune system. This immunoisolation by encapsulation has a number of important benefits for clinical application of transplantation.
First of all, it avoids the use of systemic and permanent immunosuppression. Immunosuppression has serious side effects such as a higher chance for malignancies and frequent infections. Another benefit is that encapsulation allows for successful transplantation of cells from nonhuman origin, i.e. xenografts, which could be a mean of overcoming the obstacle of limited supply of donor tissue
2. can limit the area where cells can grow, making it easy to make a safe and desired shape of tattoo.
Safe Lab Work
Korea has set up a domestic biosafety law system to strictly implement biosafety management. Biosafety refers to the appropriate use of knowledge, skills, equipment and facilities to protect the health of the experimenter and the people from potentially hazardous organisms or biological disasters for human and environmental hazards. There are various laws in these legal systems, including Living Modified Organism (LMO) laws. There are many committees that each govern to comply with the statutes concerning ‘the migration of LMO from country to country’, ‘genetic recombination experiments’, ‘prevention and management of infectious diseases’, etc. The Korea University, where our lab is located, also has established the Korea University Institute of Institutional Bioscience (KUIBC) to manage these bills so that the laboratory can implement them.
According to the guidelines for gene recombination experiments, biosafety research facilities are rated according to the biological safety grade of living organisms. Our lab (CSBL; Computational & Synthetic Biology Laboratory @ Korea univ.) is a first-class general research facility dealing with the First Risk Group (an organism known to cause no disease in healthy adults), satisfying corresponding installation and operating standards. Essential ‘installation standards’ corresponding to Grade 1 include high-pressure steam sterilizers, waste disposal facilities and experimental wastewater treatment facilities. Our laboratory has these facilities as well as safety facilities such as biosafety cabinet and eyewash. In addition, the required ‘operating standards’ of Grade I include: attaching biosafety signs, washing hands when leaving the laboratory, using mechanical pipettes during experiments, banning all activities such as food intake, food preservation, smoking or makeup, sterilization of the laboratory, completion of biosafety education, preparation and storage of records of LMOs, and preparation of waste disposal regulations, etc. Our laboratory is qualified to the laboratory by meeting these essential conditions, and therefore the laboratory's researchers also comply with their respective obligations. In order to use the laboratory, our team must first complete the minimum bio-safety training (at least 6 hours), and after familiarizing themselves with the basic safety rules of the laboratory, they always conducted experiments under the lead of the researchers.
