| Line 1,424: | Line 1,424: | ||
Talking to numerous experts in the field of phototrophic research necessitated | Talking to numerous experts in the field of phototrophic research necessitated | ||
the need for strong transcriptional termination for large genetic engineering projects. | the need for strong transcriptional termination for large genetic engineering projects. | ||
| − | <br> | + | <br> <br> |
In bacteria, two processes are responsible for proper transcript termination: intrinsic Rho-independent | In bacteria, two processes are responsible for proper transcript termination: intrinsic Rho-independent | ||
terminators, generally low energy RNA hairpins; and Rho-dependent terminators, which rely on the binding | terminators, generally low energy RNA hairpins; and Rho-dependent terminators, which rely on the binding | ||
| Line 1,432: | Line 1,432: | ||
2005]</a>. | 2005]</a>. | ||
| − | <br> | + | <br><br> |
We therefore first of all concentrated on the investigation of the natural intrinsic terminators of our | We therefore first of all concentrated on the investigation of the natural intrinsic terminators of our | ||
strain UTEX 2973. To do this, we had to take a closer look at how these intrinsic terminators function. | strain UTEX 2973. To do this, we had to take a closer look at how these intrinsic terminators function. | ||
| Line 1,441: | Line 1,441: | ||
then lower the energy of destabilization for the RNA-DNA duplex, allowing it to unwind and dissociate | then lower the energy of destabilization for the RNA-DNA duplex, allowing it to unwind and dissociate | ||
from the RNA polymerase [<i>Krebs et al.,</i> 2014]. | from the RNA polymerase [<i>Krebs et al.,</i> 2014]. | ||
| − | <br> | + | <br><br> |
It’s important to note that, especially in our organism S. elongatus, not all terminators cause complete | It’s important to note that, especially in our organism S. elongatus, not all terminators cause complete | ||
termination. In some cases, these terminators are found in between ORFs inside the same operon and might | termination. In some cases, these terminators are found in between ORFs inside the same operon and might | ||
be involved in creating complex transcription structures. From here on, however, our analysis will be | be involved in creating complex transcription structures. From here on, however, our analysis will be | ||
mainly focused on the standard case. | mainly focused on the standard case. | ||
| − | <br> | + | <br><br> |
Our first stage objective was to find promising natural terminators. In order to achieve this goal we | Our first stage objective was to find promising natural terminators. In order to achieve this goal we | ||
applied several state-of-the-art bioinformatics tools to obtain a comprehensive overview of as many | applied several state-of-the-art bioinformatics tools to obtain a comprehensive overview of as many | ||
| Line 1,538: | Line 1,538: | ||
<p> | <p> | ||
| − | Where N<sub>U</sub> = 8 is the length of the U-tract, Delta | + | Where N<sub>U</sub> = 8 is the length of the U-tract, Delta G<sub>RNA:DNA</sub> is the free-energy contribution of the |
RNA:DNA hybridization from the two nucleotides pairs at position i and i+1. | RNA:DNA hybridization from the two nucleotides pairs at position i and i+1. | ||
Revision as of 14:53, 7 December 2019
M O D E L L I N G

This year we used our mathematical and programming background to look for artificial Neutral integration Site option (aNSo) and suitable terminators for our project. We took advantage of genome data bank of UTEX2973 and used bioinformatics tools to gain insights and implement it to our project. In addition to that, we designed a model to predict the doubling times of UTEX2973 that was only possible after a thorough investigation and standardization of the current state of the art methods. To achieve this level of standardization we also implemented a light model to properly predict light intensities for our cultures.
Growth Curve Model

Growth Curve Model
Growth Curves
Synthetic Biology was created by introducing engineering principles into the previously existing
discipline of biology.
While this came with numerous advantages, one of the most important was the standardization and
characterization of parts that larger biological system are built of.
Only with this toolbox of modular, well characterized parts the current achievements in companys like
Ginkgo bioworks or the teams of the iGEM competition were made possible and the biobrick standard is a
great example.
Not only does this process allow for standardized parts, it also allows to critically question generally
agreed on methodologies that otherwise might negatively influence either the reproducibility or
performance of experiments.
However, this standardization is not fully a past achievement but an ongoing process.
We noticed during the research how to optimally grow our cyanobacteria that this process still needs
alot of standardization.
This was when we decided that we want to critically question all things currently state of the art and
this developed into a project in which we used expertise acquired in chemistry, physics, mathematics and
biology in addition to sythetic biology.
For example, in the literature the optical density of a culture is sometimes measured with the
absorption at 730 nm [Ungerer et.al. 2018] and sometimes at 750 nm [Russo et.al. 2019].
Since many labs do not have a spectrometer that is able to measure absorption at 750 nm, we decided
after valuable input from James
Goldento measure OD at 730 nm.
Light intensity measurements
One of the first aspects that we found to be unsufficiently or contradictorily documented was the light
intensity the cultures need to grow optimally.
Also, the state of the art measururement for light intensity used when describing growth of
cyanobacteria is Einstein, which is a non SI unit.
Einstein describes the number of photons that arrive in one second at an area of one square metre, one
Einstein being one mole (6.022*10**23) of photons /m2 *s.
Most of the times when this unit is used in combination with photosyntetic organisms, not all photons
are counted but only photosinthetically active photons with a wavelength betwenn 400 and 700 nanometers.
Since Einstein is not an SI unit, there are no clear definitions how to use it which opens up
possibilities for introducing errors.
Due to this for example the definition of photosynthetic photons could be a point that differs between
different research groups and is not specifically defined in most publications.
To investigate if there is a better unit to use and if so what and how it should be used, we did an
analysis of light units that we describe in the following foray:

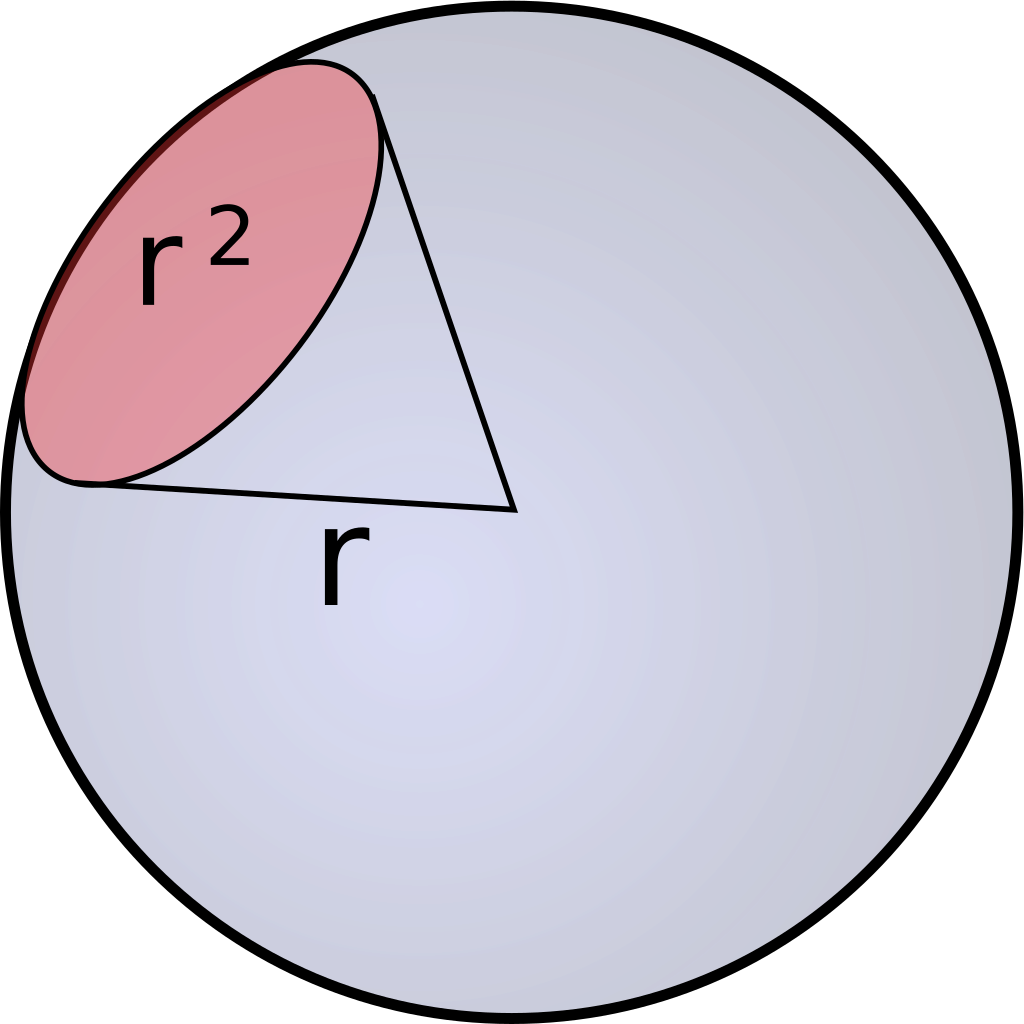
As previously mentioned, Einstein descibres the number of photosinthetically available photons (400-700nm) per square metre per second and is not the SI unit for light intenstiy (luminous flux). The SI unit is lumen, which is described as candela multiplied with the steradian. Candela is the unit for luminous intensity and steradian is the threedimensional equivalent to a twodimensional angle [Figure 2].
Candela and therefore also lumen are not only describing the intensities of different wavelenghts
and adding those up, but they are weighing them using the so called lumiosity function [Figure 1].
This function weighs each wavelength depending on how well it is recognized by the human eye and
this has huge applications in professional photography.
While this is something that is very useful when working in photography where the recognition of
the human eye is important, for photosynthetic purposes this is not useful since photons of
various wavelengths can be utilized in a similar way.
The unit Einstein, while not being an SI unit, seems to be the preferable unit for photosynthetic
purposes by now, but as previously discussed it is not accurately defined.
Einstein can also be expressed with only SI units as mol of photons of wavelengths between 400 and
700 nm per square meter per second.
In this form, there are no insecurities about the definition and while being more voluminous to
write out, we strongly believe it is much preferable.
We are still using einstein as laboratory chargon to communicate more efficiently on a daily
basis, however when it comes to scientific publications the SI unit version should be used at all
times to circumvent communication errors.
Practical light measurements
In addition to the problems using a non SI unit introduces, the process of of measurement itself is not
standardized.
The light intensity could either be measured at the lamp or at the cultures, it can be measured with the
cultures inside of the incubator, which yields lower light intensities due to their absorbance, or
without the cultures at the place they shall be at once growing.
There are two significantly different devices to measure light intensity, one with a planar sensor and
one with a spherical one.
Since the planar sensor has less area and also only measured light from one side it yields lower light
intensities than the spherical one.
Depending on the setup and how the planar sensor is used, it can also yield light intensities that are
far too high (if pointed at the lamp) or too low (if pointed at e.g. the wall).
The spherical measurement device gives both more reproducable and more accurate light intensities.
There are empirical conversion tables to convert values measured with the planar sensor to values of the
spherical measurement and vice versa, but they should be used with great caution.
Again after the valuable input of James
Golden we decided to use the spherical sensor to measure the light intensity at any given
position.
The need for a light model
Even with the spherical light sensor there are still some difficulties to overcome, for example where to place the cultures for a specific light intensity and that the light intensity has to be measured everytime before a growth curve. To solve both of these problems we decided to build a Light Model that models the light distribution in our incubator. With the help of this model we could enter the exact light intensity we wanted to grow the cultures at and multiple possible places were this light intesity was possible to achieve were given.
Light model
Our overarching goal in this year's project was the standardization in cyanobacterial research.
To this end, we have placed a strong focus on our growth curves and developed a comprehensive machine
learning model with which we were able to systematically approximate the ideal growth parameters.
But as is generally known, a model can only be as good as the data you provide it with.
In order to make our data as accurate as possible, a detailed analysis of all optimization parameters
and their implementation was required.
While some of the parameters such as CO2 were fairly easy to measure, we were particularly concerned
about the standardization of light
measurement.
For the exact measurement we have thoroughly studied this subject and came to the conclusion to measure
our complex incubator setup with a spherical light meter.
This promised us a high level of accuracy, but was associated with a significant amount of work that was
unfeasible with the amount of experiments we did this year.
Furthermore, this only allowed for discrete measurements of our setup and didn’t provide any
comprehensive overview.
To tackle this problem, a light model was desperately needed.
In the beginning we tried to address this with a simple grid approximation, but quickly realized that
this did not meet our demands for an accurate measurement and standardization.
So we looked for a better method and finally found it in numerical mathematics through so-called
splines. A spline is a special function defined piecewise by polynomials, a method which is still widely
utilised in computer science and has been used to model automobile and airplane bodies since the early
1960s. (Casteljau, (1963))
After a detailed review of the methods, we decided on so-called B-spline (basis spline) surfaces which
allows for excellent surface interpolation.
In order to use this method, a precise equidistant measurement of the incubator in the two axes was
needed. We decided to use a relatively small distance to get a high resolution map of the light
intensity. Each of these points was then carefully measured and written down to be later interpolated by
these B-splines.
In general, an order k B-spline is formed by joining several pieces of polynomials of degree k-1 with
some continuity at the breakpoints. A set of ascending breakpoints defines a so called knot vector

which determines the parametrization of the basis functions. The role of these knots will be assumed by our coordinates in one axes. Given the knot vector T, we can easily construct the associated B-spline basis function as follows:

Among other nice properties like positivity, local support, partition of unity and continuity these basis functions allow for fast and easy recursion. (Hoschek et al., 1993) We used these simple B-spline curves to construct a surface which will represent the light intensity for each point in our incubator setup. This B-spline surface is a tensor product surface defined by a topologically rectangular set of control points aij and two knot vectors U and V associated with each coordinate x, y. (de Boor et al., 1980) The corresponding B-spline surface is simply given by:

In order to check the accuracy of our model, we generated predictions for various random positions and checked them with our measuring device, yielding an incredible accuracy of ± 17 µE. In addition to the now accurate placement possibilities of each flask, the continuity of this method enabled us to generate specific contour lines which allowed us to position multiple flask at the same light intensity.


Satisfied with these results, we have used this model as the basis for the subsequent growth curves and continuously checked it for accuracy. Due to the versatility of our model we hope that it will have a meaningful impact on future iGEM teams.
Early Growth Curves
With the measurement question for light solved (for us) we started to do growth curves. Many of the publications that we used as templates for our growth curves used specialized cultivation systems that were not at our disposal. With our chosen system (of erlenmeyer flasks in our incubator) there were many adjustable parameters that we stumbled upon once we wanted to do growth curves. Many of these parameters were categorial variables, but there are also some that are numerical values. We decided to do comparative growth curves for these parameters to determine which combination of parameters allows for the best possible doubling time.
Flask Geometry
This categorical variable was a major factor to us. Limited by available space in incubators our first
growth curves were designed to evaluate which flask volume would provide best growing conditions. It
turned out that small flasks with 50ml capacity supported a growth to a higher optical density. Indeed,
at the same time cultures tend to faint into a green yellowish colour as compared to the firm green tone
of healthy S. elongatus UTEX 2973 cultures. Flasks with much higher capacities were tested too,
revealing that a high flask capacity slowed down culture growth. As cyanobacteria grow on CO2
as their primary carbon source we speculated this could be due to worse gas exchange and lower light
intensities towards the centre of the flask. From these experiments, we settled with a medium flask
capacity of 250ml.
While speculating about gas exchange another geometrical flask variant came into our minds: flasks with
baffles. They promised a high turbulence inside the flask providing higher nutrition and CO2
distribution within the fluid culture medium. However, we were concerned that to high velocities would
lead to physical damage harming our cyanobacteria. Nevertheless, we conducted the experiments. The
results are visualized in Figure 5 illustrating the positive influence of baffle flasks towards growth
rates. Due to the limited availability of flasks with four baffles we continued to use 3 baffled flasks
with a capacity of 250ml. Although they did not show much deviation from non-baffled flasks in our
experiments, we were confident that baffles support better growth rates in the long run as indicated
with smaller and therefore more CO2 restricting 100ml capacity flasks.
Lid Types
Then we had to figure out how to keep the culture safe from contamination but at the same way provide enough CO2, so that concentrations in the media could support the rapid growth of S. elongatus UTEX 2973. We took several approaches. Closing the flask opening tightly with gas permeable film under the sterile work bench seemed to us as the optimal solution. At the same time we tested foam material stuffing, rubber and transparent plastic lids (Figure 6). The rubber lid closes tightly while the plastic lid on the other hand is engineered to keep a small gap between glass and plastic allowing air to circulate. In the end we were quite surprised that the plastic lids did provide conditions that enabled the cyanobacteria to grow the fastest. Using the plastic lids was the best option for us because they not only ensured best growing conditions but also allowed for pretty easy handling of flasks when doing measurements.


Fill Volume
The fill volume had to be considered as well. Flask capacity and geometry are contributing to this factor, but we found 1/5 of the flask´s capacity the be the most feasible fill volume. Although lower fill volumes grew better based on optical density, we did not feel comfortable with these cultures because they mostly gained a yellowish tone and produced a lot of yellow foam on top when shook in the incubator. We considered the foam and the yellowish colour might be traced back to higher concentrations of cell fragments due to the fact that the turbulence seemed more violent in lower fill volumes. However, we never brought that speculation to testing. Therefore, in the future it might be interesting to assess the relation between optical density and living cell number in lower fill volumes compared to higher ones via Fluorescent activated Cell Sorting (FACS).
Culture Media
Being in contact with the cyano-community, we soon realized that a culture medium in not a culture medium, even though one is speaking from the same medium. This is owed to the fact that different laboratories use different protocols when preparing them (see link to IHP). After gathering protocols, we decided on four promising ones and tested them we (Figure 7). Off those four media, the one supporting rapid growth the best was BGM, which was adopted as the main growth medium and replaced BG11 (see link to protocols). BGM conferred a twice as fast growth within 14h after inoculation to an optical density of around 10. During media preparation, all media were buffered to a neutral pH value of around 7. Measuring pH value after 840min of growth, a lower pH value could be linked to a lower growth rate/final optical density (table 1). In which way around pH value and growth effect each other could not be clarified.

| Medium | pH value after growth of 14h |
|---|---|
| BGM | 8.21 |
| BG11 | 7.79 |
| Medium A | 8.57 |
| Medium B | 7.77 |
Growth Curves Development
Having resolved the first parameters to our growth curves many more detailed adjustments had to me made,
being updated throughout the experimental phase. As we were aiming for doubling times under 2h we came
back to literature to look for hints on how to push cyanobacterial growth rate and reproducibility.
The cultivation method has been found to be a key role in rapid cyanobacterial reproducibility. A
semi-continuous cultivation was proposed, avoiding nutrient limitations concerning for example light CO2
and trace elements [Tillich et al., 2014].
The culture is diluted at least once a day to keep optical density almost constant at reproducible
conditions. As a result, growth rate increased. For this ment diluting our cultures before doing growth
curves 2 times out of an exponentially growing preculture before inoculating the growth curve flasks.
Two inoculations were chosen as a compromise between a bearable amount of effort, as we aimed for
inoculation every 8h to keep the cultures in their exponential phase, and cyanobacterial cultures being
pushed towards rapid reproduction. A few growth curves, such as growth curves evaluated under proposed
optimal conditions and FACS-counted, up to 8 precultures were made, each inoculated out of an
exponential growing preculture.
Typically, we timed inoculation to be done when the precultures where at an optical density of 0.6 which
was considered exponential.
Another way of providing substantial nutrients for growing with rapid doubling times was the use of
modified media. BGM being modified BG11, which is used to grow fresh water strains of cyanobacteria, was
our basis medium.
It contains phosphate and nitrate concentrations equal to MAD medium. During the last period of the
project we used 5xBGM medium providing even more nutrients to the cultures.
Contrary to what has been publicized before [Włodarczyk, Selão, Norling, & Nixon, 2019] our
cultures grew better on BGM than BG11 medium (see above). W
hen inoculating cultures and diluting them with new medium, we experienced that cooled medium does delay
growth. To encounter this, we let the medium warm up to room temperature before inoculation.
The adaption to high light intensities, for instance when cultures were inoculated from plates which
were grown on lower intensities, of 1000µE to about 1800MµE was another important factor. Before growth
curves under high light conditions could be performed, the cultures were adapted to the desired
intensities by increasing intensities through the precultures.
During growth curve measurements more precautions had to be considered. When sampling cultures volumes
were taking not exceeding 0.25ml each sampling to minimize the reduction of culture throughout the
experiment. To illustrate the amount of water evaporating over the time period of 36h, equivalent to an
extended growth curve experiment we did analysis on evaporating water masses. At the same time, opening
the incubator was reduced to a minimum as well while growth curves were conducted to exclude strong
CO2 deviation.
At last, to improve statistical rigidity, for every growth curve experiment with flasks two biological
parallels, serving as the biological replicate, were cultivated. Of each biological replicate, two
technical replicates were taken.
Growth Curves Model
Variables responsible for growth
As previously described, for categorial differences one can easily do growth curves with all levels of these categories (i.e. the different lids). With this it is possible to determine, at least for the chosen parameters, which level of these categories allows for the fastest growth. In reality, all parameters that play into the growth conditions of the cultures are interlinked and change when other parameters are changed. However, for some parameters the assumption that they do not change upon changing other parameters is probably a fair approximation while drastically reducing the complexity of the investigated problem. Some categorial variables (lid type, number of schikanen in the flask) are probably mostly uncorrelated with other heavily correlated parameters (light intensity, rpm, CO2, temperature) while there are others (total flask volume, filled flask volume, medium) that are more or less correlated with these parameters. While we think that the assumption of no correlation is a fair approximation for the previously mentioned categorial variables, for the fill volume of the flask we do not think it is a good approximation. This variable that as a further approximation we chose to look at as categorical has a big influence on the amount of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the flask. However, since there were already alot of variables we had to take a look at and it is heavily correlated with the CO2 percentage that we are also investigating later, we chose to fix this parameter. This would introduce a (small) error into our model, but it would reduce the complexity and the parameters of oxygen and carbondioxide in our flask can be adjusted with the concentration of carbondioxide in the incubator. For numerical parameters (light intesity, rpm, CO2 %, temperature, filled flask volume) it would also be possible to measure certain values for each variable and use the one that fits best, but there is also the possibility to model the combined effect of these parameters on the doubling time. We did the no correlation assumption of for the previously described categorial variables (lid types, flask geometry, fill volume) and developed based on biological criteria a measurement workflow for other parameters (i.e. how many precultures are used). For four other numerical parameters (temperature, carbondioxide concentration, light intensity and shaker speed) we do think that they are heavily interlinked and decided to investigate them in conjunction with each other. We used the previously established growth curve protocol and collected datapoints varying these four parameters. Due to problems with the incubator and the time constraints going with it we were not able to collect as many datapoints as we would like.
Importance of a mathematical model for growth curve prediction
The data collected is displayed in the following table:
| doubling_time [min] | light_intensity [µmol Photons / m2 * s 400-700 nm] | shaking speed [rpm] | CO2 [%] | temp [℃] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 89.145 | 1500 | 130 | 5 | 41 |
| 1 | 100.014 | 1000 | 220 | 5 | 41 |
| 2 | 99.171 | 1500 | 220 | 5 | 41 |
| 3 | 96.956 | 1800 | 220 | 5 | 41 |
| 4 | 118.375 | 1800 | 130 | 5 | 41 |
| 5 | 113.305 | 1000 | 220 | 5 | 38 |
| 6 | 117.254 | 1500 | 220 | 5 | 38 |
| 7 | 122.141 | 1800 | 220 | 5 | 38 |
| 8 | 77.047 | 1000 | 220 | 3 | 41 |
| 9 | 81.442 | 1500 | 220 | 3 | 41 |
| 10 | 104.293 | 1000 | 220 | 5 | 43 |
| 11 | 96.914 | 1500 | 220 | 5 | 43 |
| 12 | 97.678 | 1800 | 220 | 5 | 43 |
| 13 | 102.040 | 1800 | 220 | 7 | 41 |
| 14 | 110.560 | 1500 | 220 | 7 | 41 |
With this data alone we can highlight the importance to measure these parameters in conjunction with each other. In Figure 8 there are the doubling times with three different light intensities displayed with either 38°C or 41°C as temperature. While the doubling times for the lower temperature are smaller, also the trend for the light intensity is reverted. For the high temperature the higher the intensity the lower the doubling time while for the low temperature the contrary is the case. This shows that these parameters are not independent of each other and should also be investigated not on their own but in conjunction with each other.
To investigate these parameters in conjunction with each other we decided to build a model that predicts the doubling time based on the investigated parameters.
Boundary behaviour
Something that is not part of our data are the boundaries that naturally exist for growth curves of cyanobacteria. These are partially given be the machines we are using (e.g. the maximal strength of the lamps, the maximum rpm of our shaker) and partially given by the constitution of the cyanobacteria (e.g. the maximal/minimal temperature they can grow at). With our knowledge acquired while handling this cyanobacteria, we decided on the following cutoffs:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| min light [µmol Photons / m2 * s 400-700 nm] | 100 |
| max light [µmol Photons / m2 * s 400-700 nm] | 3000 |
| min rpm | 30 |
| max rpm | 260/300 |
| min temperature | 30 [℃] |
| max temperature | 50 [℃] |
| min CO2 | 1 |
| max CO2 | 10/20 |
For light and temperature and the lower boundaries of CO2 and rpm we used cutoffs at which we are convinced that no proper growth is possible. For the upper boundaries of CO2 (10) and rpm (260) we used the highgest values that are possible due to the hardware used. For these two boundaries we also tried to increase the values further to not punish the maximal possible values too much but still incentivize our model to not use the values near the booundaries. We added one datapoint for each of these boundaries and used the most common values found in our model for the rest of the values. As example, the datapoint added for the low light and low rpm values are shown in the following table:
| doubling time [min] | light intensity [µmol Photons / m2 * s 400-700 nm] | shaking speed [rpm] | CO2 [%] | temperature [℃] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| min light | 1000 | 100 | 220 | 5 | 41 |
| min rpm | 1000 | 1500 | 30 | 5 | 41 |
We added a very high doubling time insted of a doubling time of 0 to ensure that our model has the correct behaviour in edge cases. For example, that the model predict an increased doubling time the hotter the temperature gets insted of predicting very low doubling times for those edge cases because we fed it a doubling time of 0. When we entered this data into our model, the performance was drastically reduced. We even experimented with different doubling times that we entered for this sub dataset, but for all cases tried the performance of the model was still worse than without adding this dataset in the first place. Again, due to the small amount of data that we have in the original dataset, if we add these 8 datapoints they have a huge effect on the model even outside of the boundary cases. Due to this decrease in performance we decided to not use this dataset, but we are still convinced that with enough data this would increase the accuracy of the model, especially in boundary cases.
Modelling approach
Due to the small amount of data we were able to collect we decided to use a polynomial regression model instead of a more data demanding approach like k nearest neighbors, support vector machines or neural networks. This regressional model was built using scikit learn [Pedregose et.al. 2011]. Even with this approach, the amount of data we have at our disposal is not enough to deliver a model that we would describe as accurate within and especially not outside of our training data. Nevertheless, we think a model like this is the best way forward if we want to properly predict the doubling time and with more data a very accurate model can be built. We used a common approach to polynomial regression models in that we performed a linear regression on nonlinear functions of the data. This means that we use the previously established variables (temp, rpm, light intensity, CO2) and construct the polynomial features of this dataset. For two variables x1 and x2 and a polynomial with the degree 2 this would mean we have the following values as data : [1, x1, x2, x1*x2, x1*x1, x2*x2]. This is possible due to the fact that a linear model is not limited to a linear function but to linear parameters for the variables it builds on. The code used to build this model is shown here :
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import sklearn
import operator
#from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.linear_model import LassoCV
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, r2_score
degree_polynomial = 8
size_test = 1
data_model = pd.read_csv("data_model_clean_neu.csv")
data_prep = data_model.drop("Unnamed: 0", axis = 1)
# Now I want to add data that shows the constraints of the system, so I will engineer fake data to correctly predict everything
# Format is doubling time, light, rpm, co2, temp
low_light = [1000,100,220,5,41]
high_light = [1000, 3000, 220, 5, 41]
low_rpm = [1000,1500,30,5,41]
high_rpm = [1000,1500,300,5,41]
low_co2 = [1000,1500,220,1,41]
high_co2 = [1000,1500,220,20,41]
low_temp = [1000,1500,220,5,30]
high_temp = [1000,1500,220,5,50]
boundary = []
boundary.append(high_temp)
boundary.append(low_temp)
boundary.append(high_co2)
boundary.append(low_co2)
boundary.append(high_rpm)
boundary.append(low_rpm)
boundary.append(high_light)
boundary.append(low_light)
boundary = pd.DataFrame(boundary)
boundary.columns = ["doubling_time","light_intensity","rpm","co2","temp"]
result = pd.concat([boundary, data_prep])
# Now we need to split the data into x and y
x = data_prep.drop(["doubling_time"], axis = 1)
y = data_prep["doubling_time"]
# To troubleshoot and once we have enough data, this is a very easy and sometimes faulty way to generate a train_test_split
# For an advanced train test split the sklearn functionality would be used
x_train = x[:-size_test]
x_test = x[-size_test:]
y_train = y[:-size_test]
y_test = y[-size_test:]
# Now we define the polynomial and the data that we want to predict
poly = PolynomialFeatures(degree=degree_polynomial)
light_pred = [ 1388, 1541, 1750, 1850]
rpm_pred = [ 147, 147, 147, 147]
co2_pred = [ 3.8, 3.8, 3.8, 3.8]
temp_pred = [ 40.5, 40.5, 40.5, 40.5]
to_predict = pd.DataFrame({"light_pred":light_pred, "rmp_pred":rpm_pred, "co2_pred":co2_pred, "temp_pred":temp_pred})
to_predict_pol = poly.fit_transform(to_predict)
#Now the actual model is trained as a pipeline for the polynomial features
model = Pipeline([('poly', PolynomialFeatures(degree=degree_polynomial)), ('linear', LinearRegression(fit_intercept=True, normalize = True))])
model = model.fit(x, y)
#print(model.named_steps["linear"].coef_)
predictions = model.named_steps["linear"].predict(to_predict_pol)
#print("hello")
score = model.score(x_test, y_test)
# Now the prediction is done and printed together with score and diagnose values for the model
to_predict = pd.DataFrame(to_predict)
to_predict["predictions"] = predictions
print(to_predict)
print(score)
print(predictions)
y_poly_pred = model.predict(x)
rmse = np.sqrt(mean_squared_error(y,y_poly_pred))
r2 = r2_score(y,y_poly_pred)
print(rmse, r2)
#pred_test = model.predict(x_test)
#print(pred_test)
#print(y_test)
#print(data_prep.to_html())
Again due to the lack of data normal ways of benchmarking the model like train test splits and crossvalidation are not rationally possible. If there would be more data we would use LASSO regression, because this would allow us to eliminate variables that are not useful and avoid a high variance mistake. To showcase how this model using our existing data predicts new data, we decided to predict and measure three new growth curves at unsampled regions within the boundaries of our measurement data. We decided to not calculate the minima that our model predicts, but data that is inside the range of our existing data to properly estimate how well this suboptimal model is working. The predictions of different model versions different only in the degree of polynomials used and the measured doubling time is shown in Figure 9.

As we can see in Figure 9 the prediction quality of the model is poor. The degree of the polynomial is influencing the performance of the model, but there is no clear trend visible. The data for the polynomial degree 3 was excluded since the predictions were negative. The ranking of the different doubling times is the same in all model predictions except for degree 1, with the model predicting the growth curves with the higher light intensities to show a smaller doubling time. However, not only are the predicted doubling time values significantly different from the measured ones, the measured ones are also ranked in a different order (1388>1850>1541>1750). In addition to that the spread of values is higher in the predicted doubling times compared to the measured ones. As expected, the models performance is not good enough to get quantitatively or even qualitatively correct predictions.
Summary and Outlook
During this investigation into how to grow UTEX2973 in the optimal way we stumbled upon many things that
we thought to be insufficiently documented or standardized.
We investigated how to optimally measure light intensity and thought critically about the state of the
art light units.
To make it possible to grow cultures at specific light intensities as well as to make a model of the
light intensity in our incubator to help in the everyday life of the wetlab team.
After investigating which wavelength to optimally measure the optical density of our cultures at we
started to measure comparative growth curves and developed a reproducable growth curve protocol.
For all parameters that had an effect on the growth curves of UTEX2973 we critically questioned if they
could be approximated as independent from other parameters and decided to investigate the temperature,
shaking speed, carbon dioxide concentration and light intensity in conjunction with each other.
Since the investigation of four or more different dependent parameters and their effect on the growth is
not exhaustively possible for humans we built an easily extendable model that uses polynomial regression
to predict the doubling time of various parametercombinations.

However, since measuring a single (or more) doubling time(s) is a very time demanding process, we did
not manage to collect a sufficient amount of data to train a model that is able to accurately predict
doubling times.
In addition to "just" supplying it with more data, if we have more data more steps can be done to
increase the performance of the model.
In addition to a train test split and cross validation to improve the perfomance and decrease the bias
of the model towards new data, LASSO regression can be used which would allow to investigate easily how
high dimensional the polynome the model is utilizing has to be.
The data we collected was collected only on a couple different levels for each parameter.
While this made it much easier for humans to analyse the data, for the model this drastically reduces
its usefulness.
If all datapoints were measured with more randomized values and all datapoints differ on all dimensions
of the input data, the data samples the given range much more equally.
With data like that a model can be built that is more robust due to the better sampling of the input
space.
A visual representation of the sampling in the rpm
However, for many of the parameters we cannot do that in one measurement, since the rpm, CO2
concentration and temperature has to be identical.
For the light intensity there could have been more sampling which would have improved the performance of
the model.
In addition to that, we used doubling times that we calculated by hand and by manually choosing
datapoints for the calulations.
This can also introduce an error.
By automating that process and maybe not only predicting doubling times but the optical densities at
different timepoints this manual error could be circumvented.
However, the automated calculation of doubling times can be troublesome for some suboptimal growth
curves, since the automatic definition of the exponential phase can be troublesome.
If this problem would be solved, this would take all the manual work out of the process and further
improve the model.
References
Ungerer, J., Wendt, K. E., Hendry, J. I., Maranas, C. D., & Pakrasi, H. B. (2018). Comparative genomics reveals the molecular determinants of rapid growth of the cyanobacterium Synechococcus elongatus UTEX 2973. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 115(50), E11761-E11770.Russo, D. A., Zedler, J. A. Z., Wittmann, D. N., Möllers, B., Singh, R. K., Batth, T. S., ... & Jensen, P. E. (2019). Expression and secretion of a lytic polysaccharide monooxygenase by a fast-growing cyanobacterium. Biotechnology for biofuels, 12(1), 74.
Casteljau, P. (1963). Surfaces à pôles, INPI
Hoschek, J. & Lasser, D. (1993). Fundamentals of computer-aided geometric design. Wellesley, Mass: A.K. Peters.
R., J., & de Boor, C. (1980). A Practical Guide to Splines. Mathematics of Computation, 34(149), 325.
Pedregosa, F., Varoquaux, G., Gramfort, A., Michel, V., Thirion, B., Grisel, O., ... & Vanderplas, J. (2011). Scikit-learn: Machine learning in Python. Journal of machine learning research, 12(Oct), 2825-2830.
artificial Neutral integration
Site options

Algorithm for identification of artificial Neutral integration Site options (aNSo)
As conventional neutral integration sites for cyanobacteria affect cellular fitness by knocking out
existing genes (NSI: a knockout of a flotillin CDS locus tag in S. elongatus UTEX 2973: M744_RS03615
affecting cell growth and division https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3551649/), we sought
to find new integration sites that are truly independent of the genomic and cellular context. The
identification of potential artificial Neutral integration Site options (aNSo) in the genome of
Synechococcus elongatus UTEX 2973 is paramount for the integration of orthogonal circuits and
metabolic pathways. To address this issue we developed a custom algorithm based on the Python
language.

We achieved this by processing the GenBank file (gbk) containing all of the annotated genes and
transcription start sites (TSS) of the S. elongatus UTEX 2973 genome. All lines that contained the
word “gene” along with their corresponding genomic locational information, described by indices on
the plus strand, were parsed. These indices provided information about the position of the first and
the last base of the gene, respectively. Therefore this allows all intergenic regions to be
described by the index of the last base of an upstream gene and the first base of the downstream
gene, independent on which strand the gene was located. These indices were then stored in a Python
tuple.
Subsequently, all intergenic regions shorter than 500 bp are filtered out; leaving us with eligible
sites. This was accomplished by calculating differences between the index of the start of one gene
and the index of the end of the previous gene located upstream, resulting in 56 potential aNSo.
All these potential aNSos are subsequently packaged in the tuple form and translated into a
sequence. To ensure homologous recombination, sequences with a length of at least 2500 bp were
required. The missing number of nucleotides, which could not be covered by the intergenic region,
had to be filled up with the sequence of the upstream and downstream located genes. For this, a
FASTA file containing the genomic sequence of S. elongatus Utex 2973 (Yu et al., 2015) was read into
the environment and the potential intergenic sequences were extracted based on the indices +/- the
missing nucleotides and saved additionally in the tuple.
Subsequently, the number of potential aNSo was narrowed down by excluding all sequences that
contained BsmBI and BsaI restriction sites. This was accomplished by eliminating all entries in the
tuple whose sequences contained the substrings "CGTCTC" or "GAGACG" for BsmBI restriction sites and
"GGTCTC" or "GAGACC" for BsaI restriction sites. Only 19 of 56 previously identified regions
fulfilled these criteria.
The final step of the identification of aNSo is comprised of eliminating all entries which included
a TSS in the intergenic region. Using the gbk file comprising all TSS identified in a
transcriptomics study by (Tan et al., 2018) as input, the indices of TSSs in the genome were parsed
and defined in a list. Afterwards a set was created, containing all intergenic regions which
inherited a TSS, and the tuple containing all potential aNSo was transformed into a set as well. By
subtracting the set of all TSS in intergenic regions from the set of all potential aNSo, a set was
generated containing only information about intergenic regions that do not contain BsmBI and BsaI
restriction sites and TSS. Of the previously identified 19 potential aNSo 17 contained a TSS,
leaving only two entries in the set of final aNSo fulfilling all of the required criteria. To make
the information of this final set easily accessible, a CSV file and additionally a FASTA file were
generated.
The Python script, required input files as well as the generated results can be found in our Github Repository
aNSo_1 BioBrick parts (BBa_K3228000, BBa_K3228002)
| Gene 1 start | 139038 |
|---|---|
| Gene 1 end | 139727 |
| Gene 2 start | 140309 |
| Gene 2 end | 140875 |
| Intergenic region length | 582 |
| Sequence of aNSo_1 5’ to 3’ |
TTCAAAATTTGGTGCGCTGGCAGGTCTGTGAACCGGAAACCGCGATCATGCTGGCGACCCTAGCACCTCTGCGGGCCTTGGGGGTGGATTGGTCGGATCCGCGTCTTCTCTATTTGTCCCGTCCCGTCTGTCAGCTGCTGCGCTGGCACCAGTCCGACACGGGAGAACTGACTTGGCAGAGGCTCTGCGAAAACGACGAATTACCGACTCCTACGTCGATCTAGGTCAGTCGGAATATTAGAATCGTCTGCGAAGATGCCGCCCTTGCCATGACAGCCCTCGACGACAAAACTATCGTTCGTGACTATTTCAACGCCACGGGCTTCGATCGCTGGAGCCGGATCTATGGCGATGGCGAGGTCAATTTCGTCCAGAAGAACATCCGCATTGGTCACCAGCGCACCGTCGACACCGTGCTGAGTTGGCTGGAAGCCGATGGCAATCTGAGCGATCGCAGCTTTTGTGATGCCGGCTGCGGTGTCGGCAGCCTCAGCTTACCCCTAGCACAGCGGGGGGCACAGGCCGTTTATGCCAGCGACATCTCCGCCAAGATGGTGGAAGAGGCTCGCGAGCGGGCCAGTCAGATCCCCAATTTGAACAACATTCAGCTCGAAGTTTCGGACCTTGCTTCTCTGAGCGGTCGCTACGACACCGTCATCTGTTTGGATGTGTTGATTCACTATCCAGAATCCGACGCGGCGGCCATGTTGAGCCATCTTTGCAGCTTAGCTGAGCAACGGGTTTTGGTGAGCTTCGCGCCCAAATCCCCTGTCTTGAATGTGCTCAAGCGCATTGGACAGTTCTTCCCGGGGGCCAGCAAAACGACCCGCGCATATCAGCACAGTGAAACCGCGATCGCAGCAGCCTTAGCGGCGAATGGCTTCCAAGTGCAACGTCGGGCCTTCAACAAAGCACCCTTCTATTTCTCACTTCTGCTCGAAGCTGTCCGAACTGCCTAATCAATTGTTGTTCGAGAGGTATCGCAGATTGAAGACTGAACTGGCATTTGCATTAATCAGCTGCAATCACCTCTCAGATTGACTAGACACTCAAGCATACTGAAGGTTTCAAACATCAGTAACAAGCAATAATTTTGAATTTCACAGCAACCTCAGGCGGTAGCATTGCTGCAATTAAATGGCATCTTTCGCCATACCATTCTCTACAGTTTAAGGATGTATTGTTAAATCTTTTTCTTGAGTATCGTGTATCTTCTGCATGGAATCGAATTAACTGATCAGCGATGCAAGCTGCTTCTTCTAAGAAGTAATTTTCTTGGCGTTCTTTCCGTTGTTGCTGCTTGAATATGGAAGGCCGATTATGAGGTGATTTAGGCCAAGAATTAAGTTTTTCCTTCAAGTTTTCTACTTCCCTGAGATGGCAATTAATTTTTTTGTTATCTTGGGCACGAAATAATAGGACTTGAGGATTAGGACAAGCAGTAACGGTTAAATGTGACTGCCCCCCTAAAATAGAGTATCTAGAAGAACTTTTCTTCCCCTGTTCTTTCCTAGAATCGGAGCCCGAGAGAAGAGGTGAACTACGTGGAGTAGGTAAAGTTGATCGTACCGGCAAAGACATCGAGATCAACTGCAGCTTGGCGGTTTTCTGGGGTATCTGCAGCACCACCAAGGAACCATAAAACATCTGCAGAGATACTGTAGTAGTCTTGGGTTCGTTGATAGATATCTGCAGCTTCAATTTTGGCAAGTTGACATTCACCAATAATTCGATAGCCCGTCGAGAAAACGACTGCAACATCTGCAATTCGACCATTCTTTCCAGCTTCTGAAATTGGATGTTCAATTTCAATAAACGCTTCTTGGGCATCAATCATCCCCTTATAAACTTCTTGAAAGTACTTACTGATTTCCAACTTTCCTTGCAAGTGCTCTGGAGATTCCGGATGATGTTCCATTACTGTGGTGCAAGGATGAGTATGAACAAAGTGCAATGAGGTATTTTGTCTCTTTCTGGGAAACATTAATGTTTGACAGAAAGGACAAAAAAGACTTCCTTTGGGAAAATTTTTTCTGATTTCAAGGACTGACTTAAAATCTGTCGCAAGGACTATGTTACCCTGTTGATCTTTTGCTTTGAAAGGCATGATCAAATCTATTCCTTTATTGATACTTCTCGTTTAGAGAGTCAGTATAGTCTTCTTGTAAATCCTGATCACTAGAAGTTGTTCCATGGCTTTTATCAATCCCCCCTAGTCCAGTCAACGTACCAAGAGTAATAGCCTATTTACGAGTTGGGGTCTGTTTTTGCTAAAGAAACACTGCAAAGTGCAGGATTTCATTGATCTCCTCTTCAGGTATTGTCTGGATCAGCTGATAGAGCTTTTCAGTAGCAGTCATAGATTGCAGCGCATAAGAGATCTATATTCTGAGCAATCTCGACGGATCAAGCGATTGAGCTATCGGCGGCGATGCTTGGGGGGATCGTGGCGATCGTAGAAATCGGGTGGATGGCGGCGTACCCATTTCAGAAAACGCTG |
aNSo_2 BioBrick parts (BBa_K3228001, BBa_K3228003)
| Gene 1 start | 1744903 |
|---|---|
| Gene 1 end | 1745412 |
| Gene 2 start | 1746009 |
| Gene 2 end | 1746731 |
| Intergenic region length | 597 |
| Sequence of aNSo_2 5’ to 3’ |
GTTAGTGCCTGCAGCCAAGCCCTAGAACTCCAGCCCAGCGCCGCGCGGGCTCGATATTTGCGGGCCTTGGCTTACTGGCAATTGCATCAGCCGCAAGCCGCGATCGCTGATTTACGACAAGCCTGTGATGCCTTTGCACAAGCTGGAGCAACGGTCCAACTCGATCGAGCCCGTCAGCTTCTGCAACACTGGCAGCAACAGTCCAGCCTCGTCGCCCAGGCTCCTCGCCTACAATCCAAGAACTGGCCTGGAGCTGTAACCTATGCAATGGATTTGGCGAACTGCCACGATCGCAGTCCTCTTAACGAGTTGGAGTTCTGCTGCGATCGCGCATTCCAACAATGCTGATGTCAATCAGTGTCATCACGATCGTCGCACCGGCGAATATCACTGCCACTAGGCCTGACAATAGAGTCGTTTTGATCTTTGCTGATTAGCTTCAATGATGCTTCCGACCCTGAGCACCCTGAAAACAGCGGTGCTCCTGCTTCCTTTGGCAATTCCAACGGCTGCTCTTGCCCTACCTCAAACCGCTGTTTGGCGACTGGCTGATGCTCAAAATCATCAGCACCAGAATCATCAACATCAAAGCGGGGCTGGCCATTCCCATGGCAGCTTGGCGGTGCCAACAGGCACTCCACAACCGACTGTCAATTTAGTGGTTGAACGCGACCGCAAAAGTGGTTGGAATCTCCGGCTAACTACCACTAACTTCCAGTTTGCCCCCGAGGAACTTGACAAAACAAATCGAGTTGATTCCGGGCATGCCCATTTGTTCCTTAATGGGAAAAAGATTGCGAGACTTTACGGACCTTGGTATCACTTGGCTTCGCTCCCAGCCGGGAAGCAGACTCTCATGGTGGAATTGACCAGCAATCAACACAATGTAATTACGGTTAATGGTCAACCTGTCATTGCCAAAGTGACTGTAGACGTTCCAGCGATGAAGTAATTTTCATACTGAGCTACTACGGTAGCCTCTGCCTCTCTTCCAGCAAATGGGGAGAGGCCTTGACAACTAACAGTGTTCAATCGACAGATTTTCAGACCTTGAACGATCGGATCGTAATCCTACCTGAGCGATCGTAAAATCTGTCACGGCAAAGGATATAAATACACTTGAGTTAAAGGTTTAATTCTCAGTCGCTACAGTTGTTTTTTGATTGACTGAATGAAGGTCAAGGAATCAGTTTTAGCGATAGCTTTTCAGTATTAATAATAGTAACCTTCATGCATCGGCCGTAGCTGAAAATGCAAAATAATACTTTGACTATCGTAGGCCAATATCGAGTGACTTATTGCCTGCTCTTAGTCAATGGAATAAATAAAATGCCCATCAAGCTGTCAGTGCTGGCTCGAAGCGATCTGAATCTTGTCCTAGTAGGCTAGCAAGATAATCTCGATGAGAAAAGCGATCGCCCTTAAACCAGATTTTTTGACTTTCTTGATCAATCTATTGTCCAAAAAGACCTAGGTGCGATAATTATAAAAACTATAATTCACTCTAGGGATAGAAGCTTGGCTTTGCACTCTCGTCGTTGGCTATTGATGGTGCTCACAAGCTGCTTCGCGACTAGCCTGTTCGCTAGACCTGCAATCGCTGCTGATGGCTGGTGGATCGATCAGTATGCGGTCATTCTCTTTACTGCCACGGGACGGCTCGATGCAGAACTGAAAGAAATGCGCATCGAAGGAGCCGATACGCTGCTCGTCCATGCGGATAGCCTGCCCCCACTGCTGCTACGTTGGGTTGCTTGGCGTGCCTCTCTACAGAATATGAAGTCAGTCGCCTGGGTTCAGCGTCCCACTCTCCAGCGACTCAAACATGCTAGCTCTCTCAATGGCTATGCTGCGTTGCAAGTGGATGATCACTTTTTTGCTGATCCCATTGTGAGCTTCAGTCAGCTGCGCCAAATGATTGGCAAGAAGCAGCTTTGGTGCTCTTTTCAACCGAATCAATTTTCGGAGTTTCTAGCGCGGAATTGTGATCATGTGGATGTACAAATCTACCGAATGAGTTGCCCTGCCACAATCGATTTAGCCGATAGATTGGGGTTGCTAGGTCGTCCTCAATCTGCGATCGCGGTCTATCATGATGGCACCTCTCAAGCCGATCGCGATCTCCAATGCTTCCGTCAAGCAGGTCGCGATGTTCGTAATTCAATCTTTGTTTTCAAATGGAAGAATCCAGGATCTGTCTTGTCGCGATTTTTGAAGCATCCATTAGTAGCACGACTGGAACGGATATATATTCAGCTATTTAAGGACTAGCGCTGAACTATAATCGAGCGATCAAATTTTATTGTCATCACTAAATTCTTGTGCAATTTCCCTCAAAAATTGGTTGATTTGTTGAGGCGATCGCAAATGGTAGACTTTGCGGTTTGTTCGAGCTGTCTCAATATACTCTCGATATTGAGGTGTTAATCGCTGGTGGCAAAGCCAAAGAACGCGGTAGCTACTCATTGAGCTTTTAAATAAAGGACTGTCCTCAGGCCAGC |
Terminator Model

Terminator Model
Talking to numerous experts in the field of phototrophic research necessitated
the need for strong transcriptional termination for large genetic engineering projects.
In bacteria, two processes are responsible for proper transcript termination: intrinsic Rho-independent
terminators, generally low energy RNA hairpins; and Rho-dependent terminators, which rely on the binding
of the Rho protein.
The majority of bacteria have a homolog of the E. coli Rho protein, with a few exceptions such as our
organism S. elongatus [de Hoon et al.,
2005].
We therefore first of all concentrated on the investigation of the natural intrinsic terminators of our
strain UTEX 2973. To do this, we had to take a closer look at how these intrinsic terminators function.
Rho-independent terminators typically consist of short, 7-20 base pairs long, mostly GC-rich hairpins.
The loop structure is followed by a chain of uracil residues. A protein bound to the RNA polymerase then
binds to the stem-loop tightly enough to cause the polymerase to temporarily stall. The pausing of the
polymerase coincides with the transcription of the poly-uracil region. The weak Adenine-Uracil bonds
then lower the energy of destabilization for the RNA-DNA duplex, allowing it to unwind and dissociate
from the RNA polymerase [Krebs et al., 2014].
It’s important to note that, especially in our organism S. elongatus, not all terminators cause complete
termination. In some cases, these terminators are found in between ORFs inside the same operon and might
be involved in creating complex transcription structures. From here on, however, our analysis will be
mainly focused on the standard case.
Our first stage objective was to find promising natural terminators. In order to achieve this goal we
applied several state-of-the-art bioinformatics tools to obtain a comprehensive overview of as many
candidates as possible. The software we used were:
- ARNold, which in itselfs consist of two complementary programs: Erpin (Gautheret et al., 2001); RNAmotif (Macke et al., 2001).
- TransTermHP (Kingsford et al., 2007)
- FindTerm (Solovyev et al., 2011)
Due to its design the resulting list of 2113 sequences contained many false positive and duplicate
terminator candidates.
In order to analyze the data we split it into two and ordered the sequences according to its strand. The
next step was to clear the list of possible duplicates. This was done by analyzing the intersection of
the respective bp positions. If both the intersection and the symmetric difference of two seperate
terminator candidates were non empty we expanded its definition by the difference. To redefine the
selection we later on analyzed the secondary RNA structure via kinetic modeling.
In order to filter out the misrecognized terminators from our list, we decided to use the much more
detailed transcriptomics data of both UTEX 2973 and its closely related strain PCC 7942.
Our approach was divided into two parts:
- Identify if the sequence is contained inside an open reading frame.
- Determine the approximate in vivo termination efficiency of each candidate.
For the first part of this approach we’ve taken into account the Joint Genome Institute (JGI)
predictions and transcriptionally identified ORFs. To make sure that we don’t consider wrong candidates
we decided to remove any sequence whose intersection with an ORF exceeds a threshold of 15%.
For the in vivo efficiency approximation of the sequences we calculated the relative decline in average
base counts in 25-base windows before and after the terminator candidates (Creecy et al., 2015).
Sequences which had an approximated efficiency below a high threshold of 80% were ignored for further
consideration.

After the careful separation of the unsuitable candidates we were left with the most promising
terminators. To further analyze the functions of these terminators a kinetic approach was indispensable.
The RNA secondary structures were predicted using KineFold. To choose the most likely formation we
performed multiple independent runs using different random seeds and chose the most frequent structure.

Based upon these results we were tasked with the correct identification of the U-tract, hairpin and the
A-tract regions. The predicted secondary structures were often hairpins that extended beyond the
terminator hairpin. The reason for this was the formation of base pairs between the upstream poly(A)
sequences and the U-tract. For the precise identification of these regions it was important that the
poly(U) region was part of the U-tract and not the hairpin. To correctly distinguish these two several
steps had to be taken. Given a stem loop structure, we screened for possible U-tracts in the region
between the sixth nucleotide in the 3’-arm of the stem loop and the eighth nucleotide after the stem by
evaluating every 8 base pairs.
For this we have calculated the Gibbs free energy of all possible U-tracts with the formula

Where NU = 8 is the length of the U-tract, Delta GRNA:DNA is the free-energy contribution of the
RNA:DNA hybridization from the two nucleotides pairs at position i and i+1.
The hybridization were calculated using the nearest-neighbor thermodynamic parameters at the respective
position (Sugimoto et al., 1996).
The 8bp sequence with the highest Delta GU value was then selected as the U-tract.
With the proper identification of the U-tract it was now possible for us to precisely define each
region.
| ID | Strand | Starting Site | End Site | Length | bp counts before | bp counts after | read trough | A-tract | Hairpin | Loop | U-Tract | Structure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1036 | + | 166606 | 166645 | 39 | 2182747.4 | 2.76 | 1.26E-06 | CAACUAAAGA | GAGUCGCUCAGAGAGCGGCUC | AGA | UUUUUUGUUG | (((((((((...))))))))) |
| 1000 | + | 2622887 | 2622925 | 38 | 295441.36 | 0.76 | 2.57E-06 | UAAACAACCU | CUUCAGUCACAGGACUGAGG | ACAG | GUUUUGUUUU | ((((((((....)))))))) |
| 904 | - | 2379456 | 2379414 | 42 | 585709.4 | 3.08 | 5.26E-06 | AGCAAAAAGC | CUGUCUAAGCAUUGUCUUGGACAG | CAUUGU | GCUUUUUGCU | (((((((((......))))))))) |
| 743 | - | 1899716 | 1899683 | 33 | 23739.36 | 0.16 | 6.74E-06 | UAAAAAACGC | CCGGGCAACGCUCGG | AAC | GCGUUUUUUA | ((((((...)))))) |
| 279 | - | 709603 | 709570 | 33 | 437192.08 | 12.24 | 2.80E-05 | CGAACCCCUA | GUCAUCAAUGGUGAU | CAAUG | AGGGGUUCGU | ((((((...)))))) |
| 1193 | - | 1170678 | 1170642 | 36 | 69043.84 | 7.96 | 0.000115289 | UAUCAGGAUG | UGACUGAGAACUCAAUCA | GAAC | UCCUGAUCGU | (((.(((....))).))) |
| 349 | + | 908409 | 908444 | 35 | 73266.04 | 10.08 | 0.000137581 | CAAACCCAGU | GUCUUCUUGUUGGAGGC | UUGUU | UGGGUUUUUG | ((((((.....)))))) |
| 498 | + | 1270707 | 1270744 | 37 | 134.76 | 0.04 | 0.000296824 | GGCAUUUGGG | GGGCGGCGGUGGGUCGCCC | GGUGG | UUUUUUUCUG | (((((((.....))))))) |
| 586 | + | 1518890 | 1518927 | 37 | 683.16 | 0.4 | 0.000585514 | CCACAUUAGC | GCUCUCGCCUGUCGAGAGC | CCUGU | UUUUUUAUGC | (((((((.....))))))) |
| 909 | + | 2385885 | 2385928 | 43 | 731.4 | 0.56 | 0.000765655 | GUCUAAAACC | CCGCUGGUUCCCAGAGAGCUAGCGG | CCAGA | UUUUCCUUAU | ((((((((((.....)))))))))) |
We now wanted to use these records to analyze the impact of mutations in different terminator regions.
In order to experimentally test this, we established a workflow that allows us to screen a huge
combinatorial library of terminators.
For this we have selected 3 of the strongest terminators which have mutually distinct features such as
different hairpin and loop length.
Based on research experience we have decided to include mutations in the respective U and A-tracts. The
synthetic library was ordered as degenerate oligos.
To test the terminator efficiency in vivo we build a GoldenGate Lvl2 constructs with a terminator
spaceholder surrounded by 2 fluorescent proteins.
Because of the different emitting spectra of these fluorescent proteins we will be able to measure both
independently which allows for indirect measurement of terminator strength.
For this we calculate the ratio between induced mTurquoise and induced YFP normalized by control
(plasmid with no terminator inserted).
With the help of FACS we will be able to systematically separate the different terminators and analyze
the impact of different mutations.
We hope that this approach will inspire other teams to build and screen large libraries of synthetic
parts so that the scientific community can gain a deeper insight into the inner workings of elementary
molecular building blocks.

References
Chen, J., Morita, T., & Gottesman, S. (2019). Regulation of Transcription Termination of Small RNAs and
by Small RNAs: Molecular Mechanisms and Biological Functions. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection
Microbiology, 9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2019.00201
de Hoon, M. J. L., Makita, Y., Nakai, K., & Miyano, S. (2005). Prediction of Transcriptional Terminators
in Bacillus subtilis and Related Species. PLoS Computational Biology, 1(3), e25.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.0010025
Krebs, J., Lewin, B., Kilpatrick, S. & Goldstein, E. (2014). Lewin's genes XI. Burlington, Mass: Jones &
Bartlett Learning.
Gautheret D, Lambert A. (2001) Direct RNA Motif Definition and Identification from Multiple Sequence
Alignments using Secondary Structure Profiles. J Mol Biol. 313:1003–11 (abstract).
Macke T, Ecker D, Gutell R, Gautheret D, Case DA and Sampath R. (2001) RNAMotif – A new RNA secondary
structure definition and discovery algorithm. Nucleic Acids Res. 29:4724–4735 (abstract).
Kingsford, C. L., Ayanbule, K., & Salzberg, S. L. (2007). Rapid, accurate, computational discovery of
Rho-independent transcription terminators illuminates their relationship to DNA uptake. Genome Biology,
8(2), R22. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2007-8-2-r22
V. Solovyev, A Salamov (2011) Automatic Annotation of Microbial Genomes and Metagenomic Sequences. In
Metagenomics and its Applications in Agriculture, Biomedicine and Environmental Studies (Ed. R.W. Li),
Nova Science Publishers, p. 61-78
Chen, Y.-J., Liu, P., Nielsen, A. A. K., Brophy, J. A. N., Clancy, K., Peterson, T., & Voigt, C. A.
(2013). Characterization of 582 natural and synthetic terminators and quantification of their design
constraints. Nature Methods, 10(7), 659–664. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2515
Tan, X., Hou, S., Song, K., Georg, J., Klähn, S., Lu, X., & Hess, W. R. (2018). The primary
transcriptome of the fast-growing cyanobacterium Synechococcus elongatus UTEX 2973. Biotechnology for
Biofuels, 11(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-018-1215-8
Vijayan, V., Jain, I. H., & O’Shea, E. K. (2011). A high resolution map of a cyanobacterial
transcriptome. Genome Biology, 12(5), R47. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2011-12-5-r47
Creecy, J. P., & Conway, T. (2015). Quantitative bacterial transcriptomics with RNA-seq. Current Opinion
in Microbiology, 23, 133–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mib.2014.11.011
Sugimoto, N., Nakano, S. -i., Yoneyama, M., & Honda, K. -i. (1996). Improved Thermodynamic Parameters
and Helix Initiation Factor to Predict Stability of DNA Duplexes. Nucleic Acids Research, 24(22),
4501–4505. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/24.22.4501


