Entrepeneurship
"Entrepreneurship is about being able to face failure, manage failure and succeed after failing." ― Kiran Mazumdar-Shaw
Identifying the problem
Antibiotic resistance is becoming a problem in our society. It has been predicted that in the next 30 years, 10 million people will die as a result. (1) Pharmaceutical companies like Astra Zeneca and Novartis are withdrawing their antibiotic programs. (2) The number of approvals for new antibacterial drug applications has reduced. (3) It is evident that we cannot keep up with the rate at which antibiotic resistance is growing. We need alternatives. Phage therapy has the potential to be a viable solution to this problem.
Therefore, we define our need as the development of an effective alternative to antibiotics. We propose Esther as an alternative, which will be suitable for use in the near future.
Proposition of value

Esther gives a spin to traditional phage therapy! Instead of using conventional lytic phages, we propose the use of temperate phages, that will remain dormant inside a vehicle bacteria. This non-pathogenic bacteria will be ingested by the patient, traveling throughout the gastrointestinal tract until it reaches the site of infection. Only then will the phages turn lytic and will be released right where the pathogenic bacteria are, increasing the therapeutic effect. To learn more about the design of Esther, please visit this link.
Our product will not only reduce treatment costs but will be able to stand on its own. Its core design also has the potential to be altered to cure multiple infections by simply changing the bacteriophage. Esther is a revolutionary product that will help increase the effectiveness of phage therapy as a potential treatment.
SWOT analysis

To better understand the market landscape we used a SWOT analysis, identifying Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. The strengths and weaknesses are internal factors from our own product and help us visualize where we can succeed and where we can improve. The opportunities and threats are characteristics of the potential market and help us evaluate what situations Esther will face.
Stakeholder analysis

We performed a stakeholder analysis to assess the key players involved in the market, and their relevance according to their power and interest. This was built taking into account their roles and overall impact on our project.

The key observations from the stakeholder analysis are:
- All stakeholders should be taken into account, especially if they have a big influence in the outcome of the product. For us, regulatory authorities, pharmaceutical companies and ethics groups are the main stakeholders that pose biggest barriers in entering the market.
- It is of high importance for people infected with multi-resistant bacteria to also be taken into account. This means that they are identified as a main stakeholder even with their low decission power, since they are mostly affected by the product and therefore they should have the biggest say.
- This also gives us an opportunity to look for collaborations. There was especially interest shown by Platinea cooperative at Uppsala University, drug manufacturing company Recipharm AB, and Eliava Phage Therapy Centre.
Market analysis
The global bacteriophage market had touched US$ 567.9 Million in 2017, forecasted to grow by CAGR of 3.9% from 2018 to 2026. In 2016, North America had a 37% share of the global market and became the largest regional market for bacteriophage. The key attributes that led us to select this market were a strongly established research infrastructure and existence of potential pipeline for phage therapy.
Europe is the second-largest market due to wide application of bacteriophage in food and environmental fields and stable presence of phage therapy in regions such as Georgia, Poland, and Belgium. Our alternate market, Asia Pacific is expected to witness the fastest progress in the global market; credits to the rapidly evolving biotechnology infrastructure, evolving agriculture practices, and equally supportive government initiatives1 4
1. Current trends
The key players currently engaged in the bacteriophage market include Federal State Scientific Industrial Company MICROGEN, AmpliPhi Biosciences Corporation, Phage Biotech Ltd., among others. AmpliPhi Bioscience Corporation initiated clinical trials in the U.S. for phage therapy against Pseudomonas Aerogenosa infection in cystic fibrosis in 2018.(4)
2. Market segmentation
At present, food & beverages occupy the largest revenue share in the global bacteriophage market. Bacteriophages find the widest application in food biocontrol and are presented as a natural and green method. Clinical applications of bacteriophages will witness the fastest market growth in this sector. Increased use of bacteriophages in diagnostics, phage display technology and potential use in drug discovery and development are the main attributes to the fast growth of this segment.(4)
3. Market size

- The total potential market includes the antibiotic use in livestock and patient care in humans which accounted for 131,000 tons per year. (5)
- The available market focuses on the application in humans. More than 34.8 billion defined daily doses (DDDs) of antibiotics were used worldwide in 2015 (0.5 DDD is 500 mg). (6)
- Multidrug resistant bacteria cause at least 2 million infections in the US per year. On average, the costs of additional therapeutics are $3000 per incidence. The duration of hospital stays for patients with multidrug resistant infections had prolonged from 6.4 to 12.7 days, additionally burdening the hospital and government with an extra eight million hospital days (7). Estimates regarding the medical cost per patient with an antibiotic-resistant infection range from $18,000 to $29,000. The total economic burden on the U.S. economy by antibiotic-resistant infections has been as high as $20 billion in health care costs and as high as $35 billion accounting to reduced productivity.(8)
- The penetrable market for us are infections with multi-resistant bacteria which cannot be treated with available antibiotics. Bacterial infections account for 23,000 deaths in the U.S and around 25,000 fatalities in Europe per year. (9)
The cost of antibiotic treatment per patient is estimated to be an average of $25,000 and the total penetrable market in terms of value is $12 Million.
Competitive Assessment

In order to identify the key competitors to our products, we evaluate their values to determine the strengths and weaknesses and their relevance in order to determine our position in the market. This was built taking into account their roles and overall impact on our project.
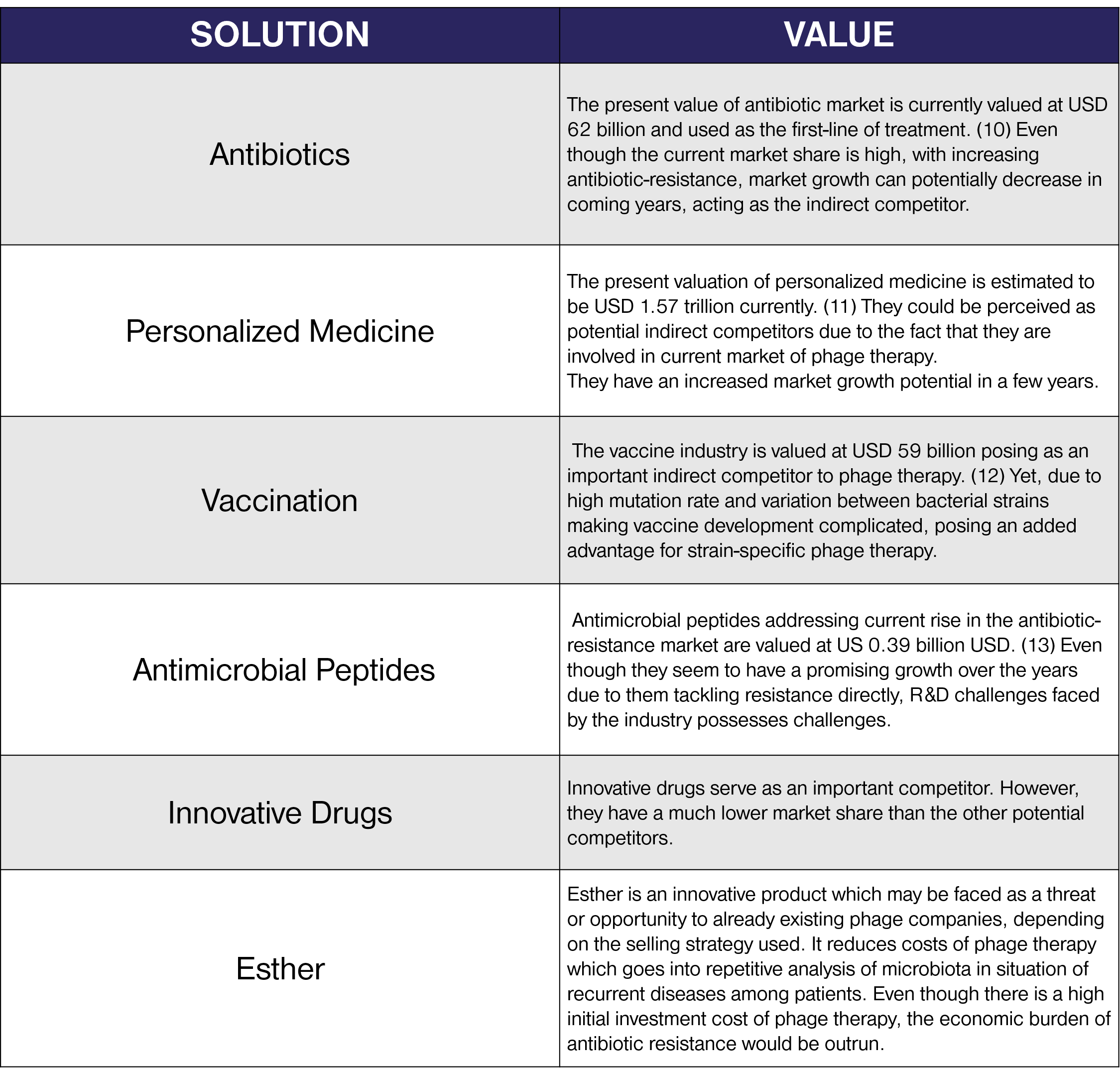
Economic evaluation
There are already existing products similar to ours which are sold as viles. We thought that in order to gain reasonable profit from our innovative product and still keep it within a reasonable pricing range to be sold to hospitals and clinics for $20. The rationale behind this was that antibiotic treatments cost a patient an average of $18 whereas Phage Therapy Centers sell the 5 viable pack at around $22.3. We don't intend to be as cheap as antibiotics and neither outrun the existing businesses in phage therapy especially phage therapy centers, for the reason of market positioning and to reduce the market entry barrier.

Professionals in academia and industry were very receptive to the introduction of ESTHER into the market and even though some skepticism about the use of a GMO as therapeutic by the general public, this might be a highly cost-effective solution in the near future which pharmaceutical and phage companies might be willing to invest in the near future.
Phage Therapy today is used as a compassionate treatment. The initial cost of investment is high but we believe that in the long run the economic burden of antibiotic resistance would be outrun the cost of phage therapy.
Gap analysis

Our product is in development stage at the moment. We will require to transform the plasmid into the bacteriophage in question and further on test the NO sensing system. The next step, once this is shown to have worked would be to move on to design the administration route and the bacterial vehicle, or serum, in which it would be administered in. Subsequently, clinical trials would be the logical step previous to our product launch, being correlated with the safety and effectiveness of the treatment and lead us to further improvements in our product.

Funding strategy
We, as a potential startup has strategized extensively on how we are going to sustain in the coming years. We have divided our strategy for the next 5 years and we have successfully achieved the first phase of funding through crowdfunding around SEK 15000 on Indiegogo and university grants like the Stockholm University grant of SEK 25,000 for developing our prototype. Universities like Karolinska Institutet, KTH Royal Institute of Technology and Stockholm University along with many other companies have sponsored our initial study in the laboratory.

Our vision
Our vision is to make sure that Phage Therapy will be a sustainable tool in battling antibiotic resistance that creates a safer tomorrow for everyone.
A Business model is the blueprint of the logic behind this vision. To be able to actualize this vision and as a part of our strategy to attract potential investors, we developed a business model that can offer a concise tool for evaluating the business and keeping the key points highly visible to us, our team and other stakeholders. For this, we have used the Business Model Canvas initially proposed by Alexander Osterwalder.

References
- Immune To Drugs: Antimicrobial Resistance Could Kill 10 Million A Year [Internet]. Forbes.com. 2019 [cited 21 October 2019]. Available from: https://www.forbes.com/sites/nicolefisher/2019/05/22/immune-to-drugs-antimicrobial-resistance-could-kill-10-million-a-year/#3e4e0a167833
- LeMieux, J. (2019). As Novartis Exits, Who Will Make New Antibiotics?. [online] GEN - Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology News. Available at: https://www.genengnews.com/insights/as-novartis-exits-who-will-make-new-antibiotics/ [Accessed 21 Oct. 2019].
- Ventola CL. The Antibiotic Resistance Crisis Part 1 : Causes and Threats. P&T. 2015;40(4):277–83.
- Credence Research, h. (2019). Bacteriophage Market Size, Share, Trend, Growth And Forecast To 2026. [online]credenceresearch.com. Available at: https://www.credenceresearch.com/report/bacteriophage-market [Accessed 21 Oct. 2019].
- Guglielmi, G. (2019). Are antibiotics turning livestock into superbug factories?. [online] Science | AAAS. Available at: https://www.sciencemag.org/news/2017/09/are-antibiotics-turning-livestock-superbug-factories [Accessed 21 Oct. 2019].
- Micreos.com. (2019). Are we ready to recognise the potential of antibiotic alternatives? - Micreos.com. [online] Available at: https://www.micreos.com/blog/Are-we-ready-to-recognise-the-potential-of-antibiotic-alternatives.aspx [Accessed 21 Oct. 2019].
- Grandviewresearch.com. (2019). Antibiotics Market Size Worth $62.06 Billion By 2026 | CAGR: 4.0%. [online] Available at: https://www.grandviewresearch.com/press-release/global-antibiotic-market [Accessed 21 Oct. 2019].
- Doughman, E. (2019). Global Vaccine Market Revenue to Reach $59.2 Billion by 2020 - Pharmaceutical Processing World. [online] Pharmaceutical Processing World. Available at: https://www.pharmaceuticalprocessingworld.com/global-vaccine-market-revenue-to-reach-59-2-billion-by-2020/ [Accessed 21 Oct. 2019].
- Goldstain research. (2019). Anti Microbial Peptides Market Outlook 2024: Global Opportunity And Demand Analysis, Market Forecast, 2016-2024. [online] Available at: https://www.goldsteinresearch.com/report/anti-microbial-peptides-market-outlook-2024-global-opportunity-and-demand-analysis-market-forecast-2016-2024 [Accessed 21 Oct. 2019].

